Aseptic Processing for Sterile Production
Aseptic processing involves sterilizing products and packaging materials separately before combining them in a sterile environment. This technique, widely used in dairy, juice, and pharmaceutical industries, relies on precise thermal processing facilitated by heat exchangers. Gasketed plate and frame, shell and tube, and tube-in-tube heat exchangers ensure rapid, uniform heating and cooling, eliminating pathogens while preserving nutritional and sensory qualities. These systems are critical for maintaining sterility, preventing contamination, and complying with FDA and EU regulations.
Applications
- Sterilization Efficiency: Gasketed plate and frame heat exchangers provide high heat transfer rates, rapidly sterilizing liquid products like milk or juices. Their compact design ensures uniform temperature distribution, eliminating microbial risks while minimizing energy use, crucial for high-throughput aseptic lines.
- Equipment Hygiene: Tube-in-tube heat exchangers, with smooth, crevice-free surfaces, prevent bacterial buildup in viscous products like sauces or pharmaceutical solutions. Their hygienic design reduces cleaning time and ensures compliance with cGMP standards, enhancing operational reliability.
- Product Integrity: Shell and tube heat exchangers handle high-viscosity or particulate-laden products, maintaining precise temperature control to preserve flavor, texture, and nutrients. Their robust construction supports continuous operation, vital for large-scale aseptic processing in food and beverage industries.
Gasketed Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
High-Efficiency Sterilization
- Modular Plates for Easy Cleaning
- High Thermal Efficiency
- Customizable for Low-Viscosity Fluids

Tube-in-Tube Heat Exchangers
Hygienic Thermal Processing
- Smooth Surfaces for Hygiene
- Ideal for Viscous Products
- Resistant to Fouling
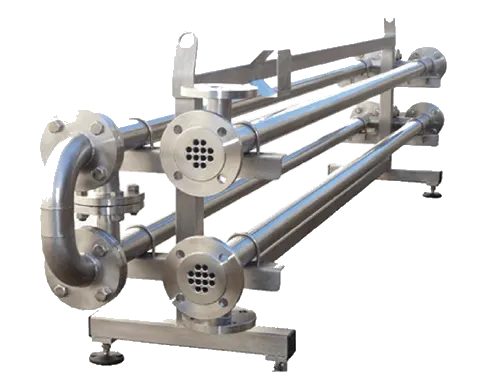
Aseptic processing is essential for producing shelf-stable products like milk, fruit juices, and injectable pharmaceuticals without refrigeration or chemical preservatives. In food and beverage production, gasketed plate and frame heat exchangers rapidly heat products to ultra-high temperatures (UHT), eliminating bacteria and spores while preserving taste and nutrition. Tube-in-tube exchangers are critical for viscous products like tomato paste or creams, ensuring gentle handling and uniform sterilization. Shell and tube designs excel in large-scale operations, processing high volumes of soups or sauces with particulates, maintaining sterility under high-pressure conditions. These systems comply with stringent regulations, such as 21 CFR Part 113 for food safety and USP standards for pharmaceuticals, ensuring consumer safety and product quality.
The success of aseptic processing depends on precise thermal management and hygienic design. Heat exchangers must achieve sterilization temperatures (typically 135–150°C) and cool products rapidly to prevent overcooking or nutrient loss. Gasketed plate and frame systems offer high heat transfer coefficients and easy disassembly for cleaning, reducing downtime in high-throughput facilities. Tube-in-tube designs minimize shear stress, preserving the texture of delicate products like yogurts or emulsions. Shell and tube exchangers, with their robust construction, handle aggressive cleaning regimes and high-pressure steam sterilization, ensuring long-term reliability. By preventing microbial contamination, these systems eliminate the need for cold chain logistics, reducing energy costs and carbon footprints.
Beyond product quality, aseptic processing enhances operational efficiency. Automated clean-in-place (CIP) systems integrated with heat exchangers minimize manual cleaning, ensuring consistent hygiene and reducing labor costs. The ability to process continuously without batch interruptions boosts throughput, making aseptic processing ideal for industries facing high demand. Additionally, the extended shelf life of aseptically processed products—often months or years—expands market reach, enabling global distribution without compromising safety or quality.


